Sparkling wine, prosaically called "bubbling wine", is very carefully categorized in Romanian wine legislation, in order to avoid misleading the consumer.
Sparkling wines classification by the bubbles origin
The fascinating bubbles in sparkling wine represent the carbon dioxide resulting from the alcoholic fermentation. They come from either the first or the second fermentation of the wine. The bubbles are kept captive in the bottles until they are released by pouring in traditional glasses (flutes or cups) or, as many connoisseurs prefer, in standard white wine glasses. Over time, wine glass designers have created at least interesting models of sparkling wine glasses, some with small outgrowths (burrs, ridges) inside, on the base, to cause pearling for as long as possible.
Wines with endogenous carbon dioxide:
- Sparkling Wine (secondary fermentation in bottle or in sealed pressure tank – acrotophor/ autoclave)
- Quality Sparkling Wine (secondary fermentation in bottle or in acrotophor)
- Quality Aromatic Sparkling Wine (secondary fermentation in bottle or in acrotophor)
- Soft Sparkling/ Pétillant/ Frizzante Wine (effervescence is obtained in the primary fermentation)
Wines with exogenous carbon dioxide:
- Brisk/ Frothy Wine (does not have a secondary fermentation)
- Fizzy Wine (does not have a secondary fermentation)
Some sparkling wines characteristics
Although the legislator put Brisk/Frothy Wine immediately after Sparkling Wine, in a classification related to the overpressure in the final product’s bottle, we present the products list based on their similarities in the winemaking process. We grouped the effervescent wines with natural bubbles, which come from fermentation, separating them from those with added gas (carbonated), carbon dioxide of exogenous origin.
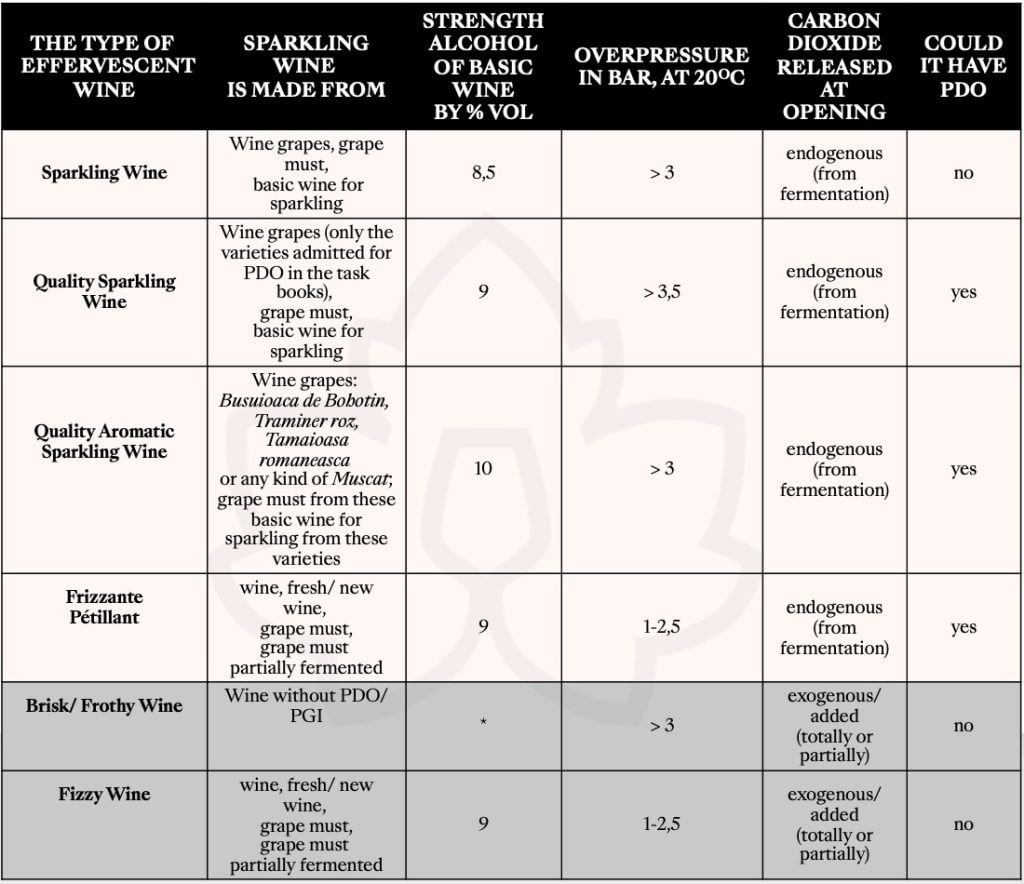
The differences between these types of wine are not given only by technical nature, but they could be appreciated visually too. Thus, the wines with natural carbon dioxide from fermentation are bubbling finely and perlage is lasting for a long time. Wines with totally or partially added carbon dioxide are more like still wines in which soda has been added, the effervescence is strong, have very short lasting pearls and disappear quickly from the glass.
Pétillant wine is also known as Frizzante Wine, as it is called in Italian. But this synonym cannot be attributed to a Fizzy Wine, which has another method of production, although this name appears (fizzy, frizzy, sparkly, bubbly) on many labels, which is neither legal nor moral.
If Sparkling Wines and Brisk/Frothy Wines are required to be bottled in special different volume bottles, Frizzante and Fizzy wines can be bottled in recipients of up to 60 liters.
Sparkling wines classification by the sugar content
For sparkling wines that must have an overpressure of at least 3 bars (sparkling wine, quality sparkling wine, quality aromatic sparkling wine and brisk/frothy wine), European and Romanian legislation stipulates that in the labeling they must be classified according to the sugar content (glucose + fructose):
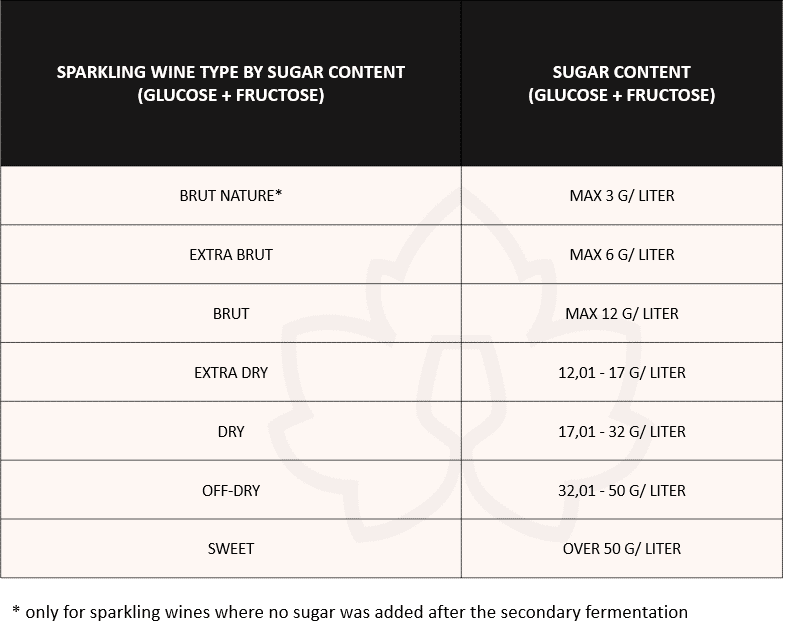
Sparkling wines specific features
- European and Romanian legislation stipulates that for Quality Sparkling Wines with Protected Designation of Origin, both the production of the raw material wine and the re-fermentation in bottles will be carried out in the area delimited for P.D.O.
- The total content of sulfites in sparkling wines cannot exceed, at the time of direct human consumption:
- 185 mg/l, for all categories of quality sparkling wines (quality sparkling wine and quality aromatic sparkling wine)
- 235 mg/l, for the other effervescent wines (sparkling without P.D.O., frizzante, frothy, fizzy).
- There are strict rules for the duration of the winemaking of sparkling wines, depending on the used method.
- sparkling wines: the duration of maintaining wine production on yeast cannot be less than 90 days (traditional method) or 30 days if the primary fermentation takes place in containers equipped with stirring devices.
- quality sparkling wines with protected designation of origin have contact with yeasts at least nine months, if the secondary fermentation that gives them the quality of sparkling wines takes place in bottles (Traditional method) and six months, if the secondary fermentation that gives them the quality of sparkling wines takes place in sealed pressure tanks (Charmat method).
- The secondary fermentation method in sealed pressure tanks is much faster, cheaper and less consuming of space and labor force. The effervescent wine reaches the consumer faster and its quality is not significantly different from that of the wine obtained through the secondary fermentation in the final bottle. However, its inclusion in a time frame makes it an industrial, impersonal, uniform and correct wine.
- The effervescent wine with the secondary fermentation in the bottle can be customized, because the duration of contact with the yeast is a minimum of nine months, no maximum time being specified. The longer this time is, the more complex the aromas that will develop in that wine will be and will represent the producer’s visit card.
Sparkling wine production by traditional method reveals the mastery of Nature, rather than the oenologist’s performance. In every bottle an exception could happen, every bottle is unique and that’s why the sparkling wines obtained by the Traditional method are sometimes considered more valuable than those obtained quickly, controlled, technically flawless, perfect.
Sursa: HOTARARE privind aprobarea Normelor metodologice de aplicare a Legii viei si vinului in sistemul organizarii comune a pietei vitivinicole nr. 164/2015



